The Choi lab published new article in Nucleic Acids Research, entitled “Structural basis for cloverleaf RNA-initiated viral genome replication” (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37486760/)
Dr. Gottipati and graduate student Sean McNeme are the co-first authors.
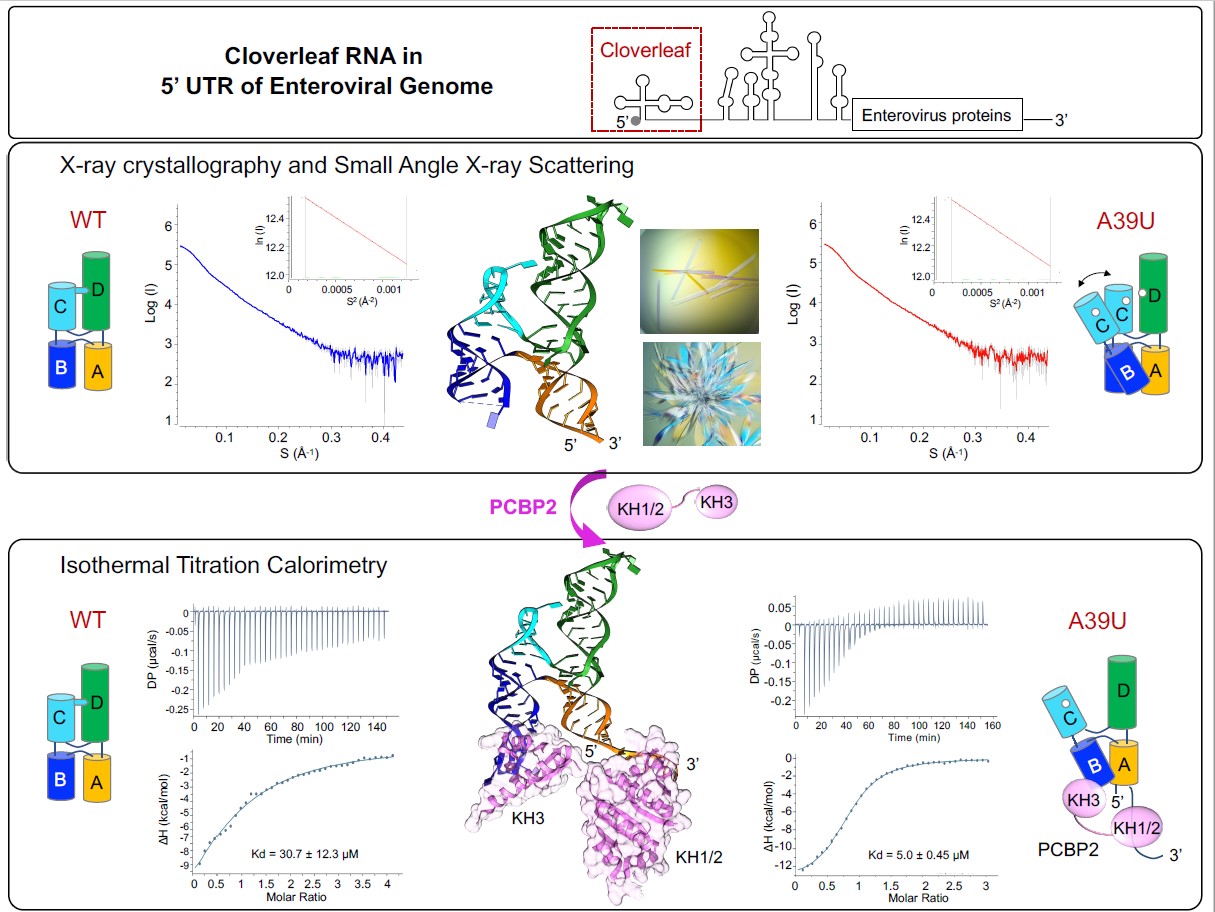
Abstract: The genomes of positive-strand RNA viruses serve as a template for both protein translation and genome replication. In enteroviruses, a cloverleaf RNA structure at the 5' end of the genome functions as a switch to transition from viral translation to replication by interacting with host poly(C)-binding protein 2 (PCBP2) and the viral 3CDpro protein. We determined the structures of cloverleaf RNA from coxsackievirus and poliovirus. Cloverleaf RNA folds into an H-type four-way junction and is stabilized by a unique adenosine-cytidine-uridine (A•C-U) base triple involving the conserved pyrimidine mismatch region. The two PCBP2 binding sites are spatially proximal and are located on the opposite end from the 3CDpro binding site on cloverleaf. We determined that the A•C-U base triple restricts the flexibility of the cloverleaf stem-loops resulting in partial occlusion of the PCBP2 binding site, and elimination of the A•C-U base triple increases the binding affinity of PCBP2 to the cloverleaf RNA. Based on the cloverleaf structures and biophysical assays, we propose a new mechanistic model by which enteroviruses use the cloverleaf structure as a molecular switch to transition from viral protein translation to genome replication.

 The College of Arts
The College of Arts